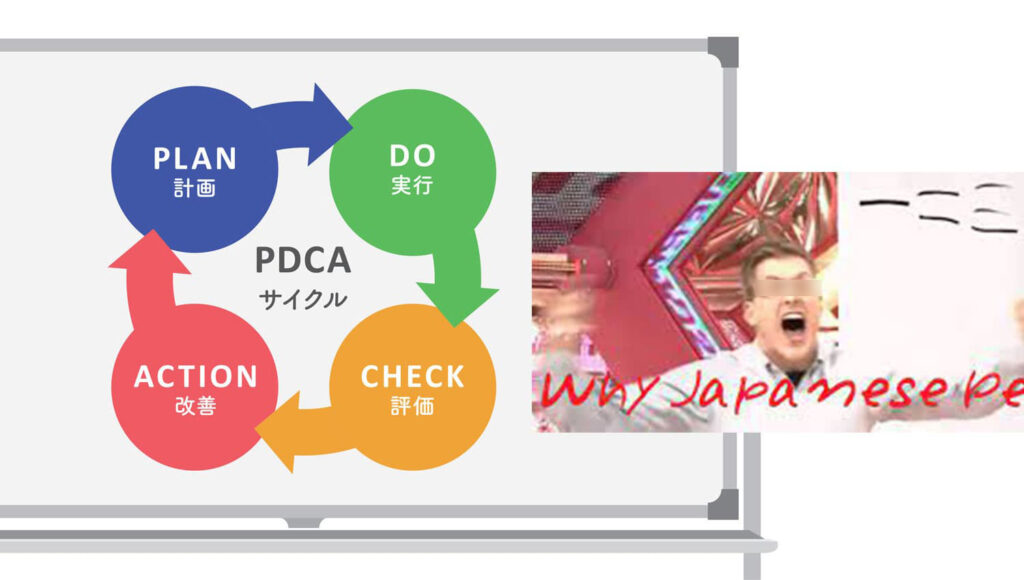
近年、PDCA(Plan-Do-Check-Act)サイクルは、多くの組織や個人において目標達成やプロジェクト管理の手法として広く知られてきました。しかし、時代の変化と共に、新たな目標達成術「IOIFサイクル」が注目を集めています。
IOIFサイクルは、Innovate(革新)、Observe(観察)、Implement(実施)、Fine-tune(微調整)の4つのフェーズで構成されています。PDCAと同様に、IOIFサイクルも目標達成に向けた反復的なプロセスを促進しますが、いくつかの異なる側面があります。
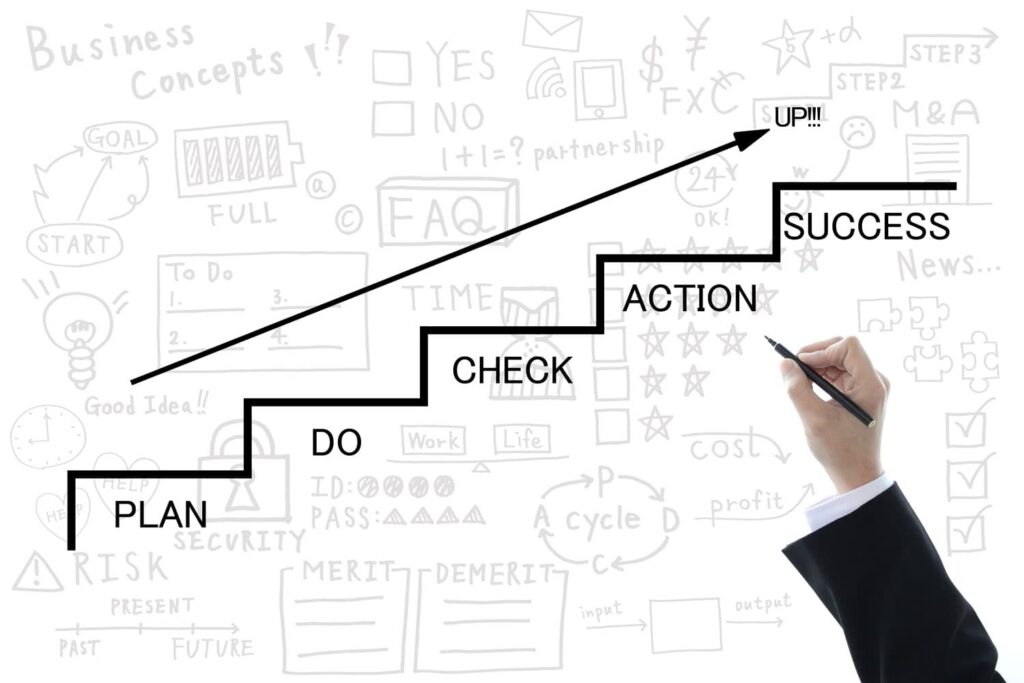
まず、IOIFサイクルの最初のフェーズである「Innovate(革新)」は、PDCAの「Plan(計画)」に相当しますが、よりアイデア創出や革新的なアプローチに焦点を当てます。従来の計画作成に留まらず、問題解決や目標達成に向けた新たなアイデアや戦略を生み出すことが重要です。
次に、「Observe(観察)」フェーズでは、結果の観察とデータ収集が重要な役割を果たします。PDCAの「Check(チェック)」に相当するこのフェーズでは、目標に対する進捗状況や効果を客観的に評価し、改善の方向性を見出すことが求められます。
「Implement(実施)」フェーズでは、PDCAの「Do(実行)」に相当しますが、より迅速で効果的な実装を重視します。IOIFサイクルでは、実施段階での迅速な行動と実験的なアプローチが重要視されます。失敗から学び、素早く修正しながら進むことが特徴です。
最後に、「Fine-tune(微調整)」フェーズでは、PDCAの「Act(改善)」に相当しますが、より継続的な改善と微調整を重視します。IOIFサイクルでは、実施した戦略やアクションに対するフィードバックを継続的に収集し、次のイテレーションでの改善につなげることが重要です。

PDCAは確かに優れた目標達成手法であり、多くの成功事例を生み出してきました。しかし、時代の変化に伴い、IOIFサイクルのような新たなアプローチが登場し、注目を浴びています。IOIFサイクルはより革新的で迅速なプロセスを提供し、現代の複雑なビジネス環境に適した手法と言えるでしょう。
重要なのは、PDCAやIOIFサイクルなどの手法を単純に採用するのではなく、組織や個人のニーズや状況に合わせて柔軟に適用することです。目標達成に向けた最適な手法を選択し、継続的な改タイトル: Is PDCA Outdated? Introducing the Latest Goal Achievement Method: IOIF Cycle
In recent years, the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle has been widely recognized as a methodology for goal achievement and project management in many organizations and individuals. However, with the changing times, a new goal achievement method called the “IOIF Cycle” is gaining attention.
The IOIF Cycle consists of four phases: Innovate, Observe, Implement, and Fine-tune. Similar to PDCA, the IOIF Cycle facilitates an iterative process towards goal achievement, but with some distinct aspects.
Firstly, the “Innovate” phase of the IOIF Cycle corresponds to the “Plan” phase of PDCA but emphasizes idea generation and innovative approaches. It goes beyond traditional planning and encourages the creation of new ideas and strategies for problem-solving and goal attainment.
Next, the “Observe” phase emphasizes result observation and data collection. This phase, equivalent to PDCA’s “Check” phase, involves objectively evaluating progress and effectiveness towards the goals and identifying directions for improvement.
The “Implement” phase, corresponding to PDCA’s “Do” phase, prioritizes swift and effective implementation. In the IOIF Cycle, rapid action and an experimental approach are emphasized. It involves learning from failures, making quick adjustments, and moving forward.
Lastly, the “Fine-tune” phase, equivalent to PDCA’s “Act” phase, focuses on continuous improvement and fine-tuning. In the IOIF Cycle, continuous feedback collection on implemented strategies and actions is crucial for driving improvements in subsequent iterations.
PDCA has undoubtedly been an excellent methodology for goal achievement, generating numerous success stories. However, as times change, new approaches such as the IOIF Cycle have emerged and gained attention. The IOIF Cycle offers a more innovative and agile process, suited for the complexities of the modern business environment.
What’s important is to not merely adopt methodologies like PDCA or the IOIF Cycle in a rigid manner but to apply them flexibly based on the needs and circumstances of organizations and individuals. Choosing the most suitable methodology for goal achievement and embracing continuous improvement is key to success in today’s dynamic landscape.